In today’s competitive digital landscape, standing out in search results isn’t just important—it’s essential for survival. While you’re busy optimizing content and building backlinks, there’s a powerful SEO technique that many beginners overlook: schema markup.
This hidden weapon in your SEO arsenal can transform how search engines see and display your content. By implementing structured data, you’re essentially giving Google a roadmap to your website’s most valuable information. The result? Rich snippets that capture attention, communicate value, and drive qualified traffic to your site.
If you’ve been struggling to increase your click-through rates despite having quality content, schema markup could be the missing piece of your SEO puzzle. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know—from understanding what schema markup is to implementing it correctly and measuring its impact on your traffic.
Ready to gain a competitive edge? Let’s unlock the power of schema markup together.
What is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is a form of microdata that you add to your website’s HTML. It helps search engines understand the context of your content better. Think of schema markup as a translator that converts your content into a language search engines can easily understand.
When you implement schema markup, you’re essentially giving search engines specific instructions about your content. This extra layer of information helps search engines display your content as rich results in search engine results pages (SERPs).
For example, if you’ve ever seen star ratings, prices, or availability information directly in search results, that’s schema markup at work. By providing this structured data, you make it easier for users to find exactly what they need.
Why Schema Markup Matters for SEO
Schema markup is not a direct ranking factor. However, it can significantly improve your click-through rates (CTR) and drive more inbound traffic to your website. Here’s why schema markup matters for your SEO strategy:
- Enhanced SERP Listings: Schema markup helps your content stand out in search results with rich snippets. These eye-catching results attract more clicks than standard blue links.
- Better User Experience: By providing detailed information directly in search results, you help users make informed decisions before they even visit your site.
- Higher Click-Through Rates: Research shows that rich results can increase CTR by 30% or more compared to standard search results. More clicks mean more traffic to your website.
- Reduced Bounce Rates: When users know what to expect before clicking, they’re less likely to bounce back to the search results. This improved user engagement signals to Google that your content is valuable.
- Voice Search Optimization: As voice search continues to grow, schema markup helps your content become more discoverable through voice assistants like Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant.
Types of Schema Markup You Should Know

Schema.org (the collaborative community behind schema markup) offers hundreds of markup types. Here are the most useful schema markup types for boosting your inbound traffic:
Organization Schema
This tells search engines about your business information, including your name, logo, contact details, and social media profiles. It helps build brand recognition and trust.
Local Business Schema
If you have a physical location, this schema type is crucial. It displays your address, phone number, business hours, and reviews directly in search results. Perfect for local SEO!
Product Schema
E-commerce sites can benefit from product schema that shows pricing, availability, and review ratings. These rich results catch the shopper’s eye and drive qualified traffic.
FAQ Schema
This displays a list of questions and answers directly in search results. It’s great for capturing more SERP real estate and addressing user queries before they even click.
How-To Schema
Perfect for tutorial content, this schema type shows step-by-step instructions in search results. It’s highly effective for DIY and instructional content.
Review Schema
This displays star ratings and review counts, which can significantly increase trust and click-through rates for your product or service pages.
How to Implement Schema Markup: Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing schema markup might sound technical, but it’s easier than you think. Follow these steps to add schema markup to your website:
1. Choose Your Schema Type
First, identify which type of schema markup best suits your content. Visit Schema.org to explore available schema types and properties.
2. Generate Your Schema Code
You have three format options for schema markup: JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa. Google recommends JSON-LD because it’s easier to implement and doesn’t interfere with your HTML structure.
Use these tools to generate your schema code:
- Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
- Schema.org’s Schema Markup Generator
- Structured Data Testing Tool
3. Add the Schema Code to Your Website
For JSON-LD (recommended method), add the generated code to the <head> section of your HTML. If you’re using WordPress, plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math make this process even simpler.
Here’s an example of JSON-LD schema markup for a local business:
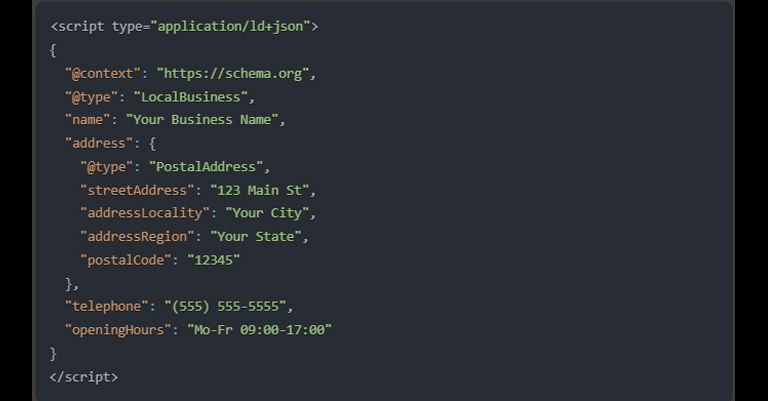
4. Customize Your Schema Properties
Add as many relevant properties as possible to provide complete information. The more details you include, the better search engines can understand and display your content.
Testing Your Schema Markup
Before going live, it’s essential to test your schema markup. Here are the tools you should use:
- Google’s Rich Results Test: This tool shows how your page may appear in Google search results and identifies any errors in your markup.
- Schema.org Validator: Use this to check if your schema markup follows the official Schema.org guidelines.
- Google Search Console: After implementing schema markup, monitor the “Enhancements” section to track how your rich results perform over time.
Make sure to fix any errors or warnings these tools identify. Invalid schema markup won’t help your SEO efforts and might even hurt them.
Common Schema Markup Mistakes to Avoid

Even experienced SEO professionals make mistakes with schema markup. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Using Inappropriate Schema Types: Only use schema types that truly match your content. Misleading markup can lead to penalties.
- Incomplete Information: Fill out as many properties as possible. Bare-minimum schema markup won’t give you the best results.
- Outdated Information: Keep your schema markup updated, especially for time-sensitive content like events or special offers.
- Inconsistent NAP Data: For local businesses, ensure your Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) are consistent across all schema markup and online listings.
- Ignoring Mobile Optimization: Rich results are even more important on mobile. Test how your schema markup appears on mobile search results.
Measuring the Impact of Schema Markup on Traffic
To determine if your schema markup implementation is working, track these metrics:
- Click-Through Rate: Compare your CTR before and after implementation. You should see an increase after adding schema markup.
- Impressions: Monitor if your pages appear in search results more frequently.
- Search Rankings: While schema markup isn’t a direct ranking factor, the increased engagement it drives can positively influence your rankings.
- Rich Result Performance: In Google Search Console, track how often your pages appear as rich results and how many clicks they generate.
- Conversion Rates: Ultimately, you want to know if the additional traffic is converting. Set up goal tracking in Google Analytics to measure this.
Schema Markup Best Practices
Follow these best practices to maximize the impact of your schema markup on inbound traffic:
- Start with Your Most Important Pages: Focus on high-value pages first, such as your homepage, product pages, and key service pages.
- Be Specific and Accurate: Use the most specific schema type possible. For example, use “MedicalClinic” instead of just “LocalBusiness” if applicable.
- Combine Schema Types When Appropriate: You can use multiple schema types on a single page when relevant. For example, a restaurant can use both LocalBusiness and Menu schema.
- Update Your Schema Regularly: Keep your schema markup current, especially for time-sensitive information like events or special offers.
- Follow Google’s Guidelines: Always adhere to Google’s structured data guidelines to avoid penalties and ensure your rich results display properly.
Conclusion
Schema Markup is one of the most underutilized SEO strategies that can significantly boost your inbound traffic. By helping search engines understand your content better, you improve your visibility in search results and attract more qualified visitors to your website.
Remember, implementing schema markup is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Start with the most critical pages on your site, monitor the results, and continuously refine your approach.
The extra effort you put into schema markup implementation will pay off with increased visibility, better click-through rates, and ultimately more conversions. Take action today, and you’ll gain a competitive edge in the increasingly crowded digital landscape. Are you ready to boost your inbound traffic with schema markup? Follow the steps outlined in this guide, and you’ll be well on your way to better search visibility and more qualified website visitors.




