Key SEO Terms: The Ultimate List You Need to Know
Welcome to the ultimate collection of key SEO terms. Knowing the following terms is vital, whether you’re a seasoned expert or just starting with SEO. This resource explains the most important words and ideas in a way everyone can understand. Check out the list below to learn more and improve your online presence today!
Why Know These SEO Terms?
Knowing and understanding essential SEO terms is crucial because they help you navigate the world of online marketing. These terms are the building blocks of strategies that can improve your website’s visibility on search engines like Google. When you understand these terms, you can make informed decisions, optimize your content, and drive more traffic to your site. This leads to better engagement, higher rankings, and more success for your online presence.
All the SEO Terms You Need to Know

On-Page SEO
On-page SEO involves changes to a webpage to help it rank better on search engines like Google. It’s like cleaning your room and putting things in the right place so it’s easy to find. For a webpage, this means using the right words in titles, headings, and text. It also means making sure pictures have good names and making the page easy to understand. Good on-page SEO helps a webpage rank higher. This, in turn, improves the chances that users will click your link.
10x Content
10x content refers to content that is 10 times better than what’s already available online. It provides exceptional value by being more detailed, engaging, and helpful than other similar content. This type of content stands out because it is well-researched, easy to understand, and offers unique insights. 10x content not only attracts more traffic but also builds trust and authority in the industry. By exceeding audience expectations, it helps improve SEO rankings and drives more conversions.
Alt Text
Alt text is a short description of an image that appears on a website. It helps people understand what the picture shows if the image doesn’t load. Let’s say you have a picture of a dog. The alt text might say, “A brown dog playing with a ball.” Alt text also helps people who use screen readers, like those who are visually impaired. It reads the description aloud so they know what’s in the picture. Additionally, alt text helps search engines understand the content of the image, which can improve the website’s search rankings.
Anchor Text
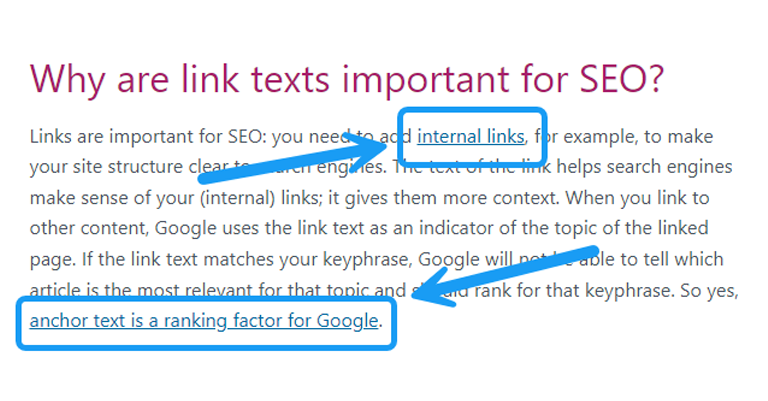
Anchor text is the clickable word or phrase in a link on a website. It usually stands out in a different color or is underlined. When you click on the anchor text, it takes you to another page or website. For example, if you see the words “learn more” in blue, that’s anchor text. The words you choose for anchor text are important because they help search engines understand what the linked page is about. Using clear and relevant anchor text can improve how well a page ranks in search results.
Bounce Rate
Bounce rate is the percentage of people who visit a webpage and leave without clicking on anything else. Imagine someone coming to your house, looking around for a moment, and then walking out the door without talking to anyone or exploring further. In the same way, a high bounce rate means many visitors don’t stay or explore more pages on your site. A lower bounce rate is better because it means visitors are finding your content interesting and are staying longer.
Breadcrumbs
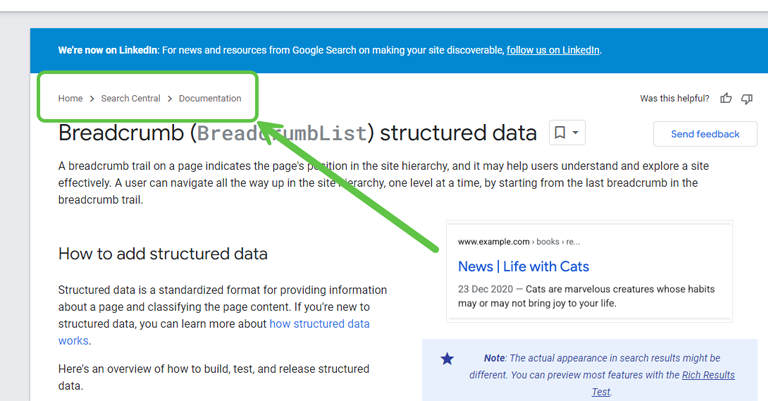
Breadcrumbs are small links at the top of a webpage that show you where you are on a site and help you find your way back. They look like a trail of crumbs that you can follow. For example, if you’re on a page about “Cats” and it’s part of a “Pets” section, you might see breadcrumbs like this: Home > Pets > Cats. This helps you understand where you are and easily go back to the “Pets” section or the main “Home” page.
Canonical Tag
A canonical tag that tells search engines which version of a page is the main one. Sometimes, the same content appears on different pages or URLs, confusing search engines. The canonical tag helps fix this by pointing to the original or preferred version of the page. Let’s say you have two pages with similar content. The canonical tag lets search engines know which to show in search results. This helps avoid duplicate content issues and ensures that the right page gets the best ranking.
Canonical Tag
Click-through rate (CTR) shows how many people click on a link compared to how many see it. For example, if 100 people see your link and 10 of them click on it, your CTR is 10%. It helps you know if your link is interesting and makes people want to click. A higher CTR means more people are clicking on your link, which is good for getting more visitors to your webpage.
Content Clusters / Topic Clusters
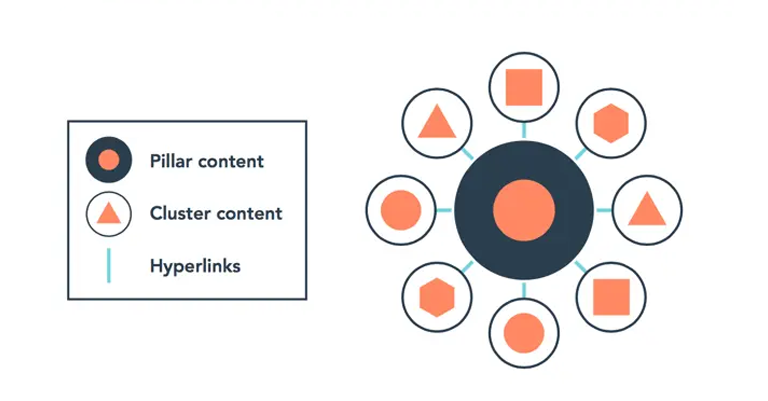
Content clusters (aka topic clusters) are groups of related web pages that focus on a main topic and its subtopics. It’s like a big book with different chapters. For example, if your main topic is “Healthy Eating,” you might have pages about “Fruits,” “Vegetables,” and “Healthy Recipes.” Each page links back to the main topic and to the other pages. This helps search engines understand your site has lots of useful information about the main topic. It also makes it easier for people to find what they’re looking for.
Content Freshness
Content freshness measures how current your website information is. If you keep your content current with the latest facts and trends, it is considered fresh. For example, if you have a blog post about “Summer Fashion Trends” and update it each year, it stays fresh. Search engines like Google prefer fresh content because it’s more relevant and useful for people looking for the latest information.
Content Silos
Content silos are a way of organizing information on a website into separate sections or categories. Imagine a bookshelf with different shelves for different types of books. On a website, content silos help group related topics together so it’s easy to find and understand. For example, a site about pets might have silos for “Dogs,” “Cats,” and “Birds,” with each silo containing all the related pages about that topic. This helps both people and search engines find and navigate the content more easily.
Duplicate Content
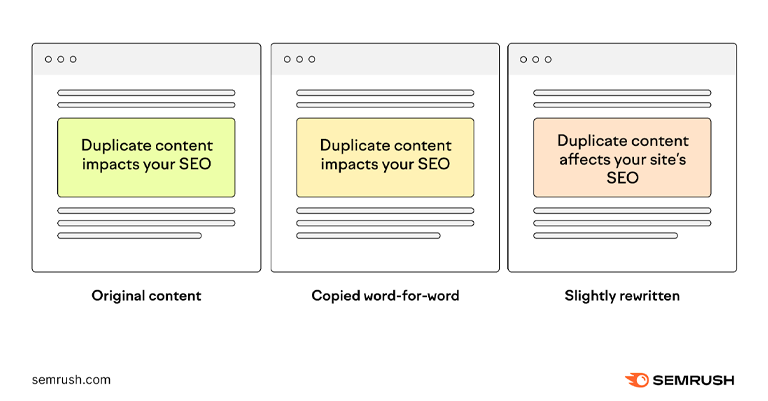
Duplicate content happens when the same text or information appears on more than one webpage. It’s like having two copies of the same book in a library. Search engines might not know which page to show in search results if they see the same content on different pages. Creating unique content for each page helps search engines understand what makes each page special. It also makes it easier for people to find what they’re looking for.
Header Tags (H1, H2, etc.)
Header tags organize and title different sections on a webpage. Use H1 for the main title of the page, similar to a big headline on a poster; H2 for main sections under the title, like subheadings in a book; and H3 and other tags for smaller sections within the H2 sections, like chapter titles in a book. Using header tags helps both people and search engines understand the important parts of your page and how the content is organized.
Image Optimization
Image optimization means making your pictures on a website load faster and look good. This involves reducing the file size of the images without making them blurry. It also means using the right file names and adding alt text to describe the images. This helps the webpage load quickly, improves user experience, and makes it easier for search engines to understand what the images are about.
Internal Links
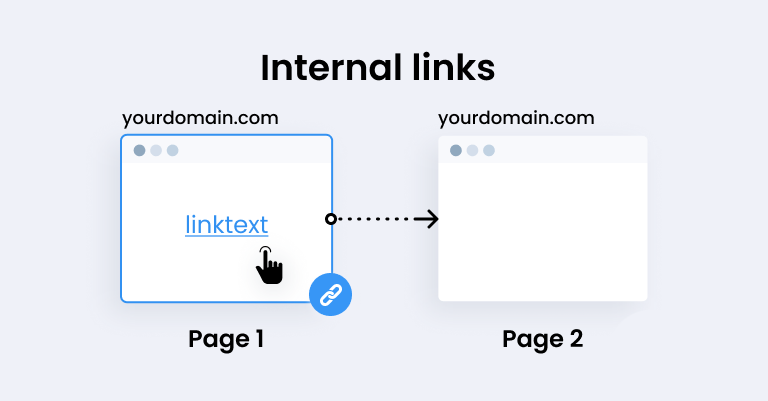
Internal links are clickable words or phrases on a webpage that take you to other pages within the same website. They help you easily navigate around the site. For example, if you’re reading a page about “Healthy Recipes” and see a link to “Vegetable Dishes,” clicking on it will take you to a page on the same site about vegetable recipes. Internal links guide both people and search engines to explore more content on your website. They improve the user experience and help search engines understand the structure of your site better.
Keyword Cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization happens when multiple pages on a website target the same keyword or topic. This confuses search engines about which page should rank higher. It’s like having several people try to grab the same prize, making it hard for anyone to win. To fix this, you should make sure each page focuses on different keywords or topics to help search engines understand which page is the most important for each search term.
Keyword Density
Keyword density is how often a writer includes a specific word or phrase on a webpage compared to the total number of words. It’s like counting how many times a word appears in a story. If you use a keyword too much, it can seem unnatural and might not be helpful. However, using it the right amount helps search engines understand what your page is about. This can improve your page’s ranking in search results.
Keyword Placement

Keyword placement is where you put specific words or phrases on a webpage to help it rank better in search results. It’s like putting important items in a visible spot so everyone can see them. You should use keywords in important parts of your page, like the title, headings, and the first few sentences. This helps search engines understand what your page is about and makes it easier for people to find your content when they search online.
LSI Keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing)
LSI keywords are words or phrases related to the main topic of a webpage. They help search engines better understand your content. For example, if your main topic is “healthy eating,” LSI keywords might include “nutritious foods” or “balanced diet.” Using LSI keywords makes your content more relevant and clearer for search engines. This can help your page appear in more search results, improving its visibility. Including LSI keywords also enhances the user experience by covering related topics that users may find helpful.
Meta Description
A meta description is a short summary of a webpage that appears in search engine results. It usually includes a few sentences that describe what the page is about. Think of it like a movie trailer that gives you a sneak peek of what’s inside. A good meta description helps people decide if they want to click on the link to visit your page and can help improve how your page appears in search results.
Mobile Responsiveness

Mobile responsiveness means making sure a website looks good and works well on phones and tablets. It’s like adjusting a picture frame so it fits perfectly on different walls. A mobile-responsive site changes its layout and design to fit various screen sizes, making it easy for users to read and navigate on any device. This helps keep visitors happy and can improve how well your site ranks in search results.
Outbound Links
Outbound links are clickable links on your webpage that direct visitors to other websites. For example, if your page about healthy recipes includes a link to a nutrition website, that’s an outbound link. These links guide your readers to additional information and resources related to your content. Outbound links can also boost your site’s credibility by connecting to trustworthy and authoritative sources. They help search engines understand the context and relevance of your content by showing that you’re offering valuable information. Including well-chosen outbound links improves your site’s overall user experience and trustworthiness.
Page Load Speed

Page load speed is how quickly a webpage opens and displays its content when someone clicks on it. Imagine waiting for a book to open; if it takes a long time, it’s frustrating. Similarly, if a webpage takes too long to load, visitors might get bored and leave before seeing anything. Faster page load speeds improve user experience by making the site more enjoyable and easier to use. Search engines also prefer faster pages and may rank them higher in search results. Improving page load speed involves optimizing images, reducing unnecessary code, and using efficient web technologies.
Readability
Readability is how easy it is for people to read and understand the text on a webpage. It involves using clear and simple language, short sentences, and a logical structure. Good readability means organizing text with headings, bullet points, and short paragraphs so readers can quickly find key information. Avoiding complex jargon or technical terms helps prevent confusion. Improving readability makes the content more engaging and easier for visitors to follow. This enhances their overall experience and helps them find the information they need more efficiently.
Rich Snippets
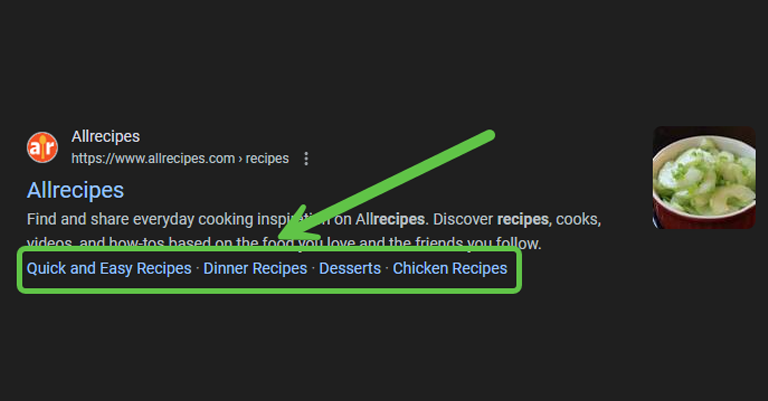
Rich snippets are extra details that show up in search engine results to give users more information about a webpage. They can include star ratings, reviews, or images that make the webpage stand out. For example, if you search for a recipe, a rich snippet might show a picture of the dish, cooking time, and user ratings. These snippets help people see useful information before clicking on the link. They also help search engines understand what the page is about, which can improve its chances of appearing in search results. Rich snippets enhance both the user experience and the visibility of your webpage.
Schema Markup
Schema markup is special code added to a webpage to help search engines better understand the content. It provides extra details about what’s on the page. For example, if you have a recipe on your site, schema markup can tell search engines the cooking time, ingredients, and nutrition facts. This extra information helps search engines show more detailed results, like rich snippets, in search results. Using schema markup makes it easier for search engines to understand and display your content in a way that’s more helpful for users. This can improve how your page appears in search results.
Structured Data
Structured data is a way of organizing information on a webpage so search engines can understand it better. It uses a special code to describe different parts of the content, like names, dates, or locations. For example, if you have a movie review on your site, structured data can help search engines know the movie’s title, release date, and ratings. This makes it easier for search engines to show more detailed and accurate results, like rich snippets, in search results. By using structured data, you help search engines present your content in a way that is more useful and engaging for users.
Time on Page
Time on page measures how long visitors stay on a single webpage before moving to another page or leaving the site. It’s like timing how long someone reads a book before stopping. A longer time on page usually means visitors find the content interesting or engaging. A short time might suggest the content didn’t meet their needs or wasn’t engaging enough. Monitoring time on page helps website owners see how well their content performs. It also provides insights on how to improve the user experience to keep visitors interested longer. This can lead to better website engagement overall.
Title Tag
A title tag is a short text at the top of a web browser and in search engine results. It tells visitors and search engines what a webpage is about. For example, if your page is about “Easy Chocolate Cake Recipes,” use “Easy Chocolate Cake Recipes – Delicious and Simple” as the title tag. A good title tag is clear, includes essential keywords, and encourages clicks. It helps search engines know which pages are relevant for specific searches. This can improve how well your page ranks in search results.
URL Structure
URL structure refers to the way web addresses are organized on a website. It’s like the layout of an address on an envelope that helps you find a specific place. A good URL structure uses clear and simple paths to show where a page is located. For example, a URL like “www.example.com/healthy-recipes” clearly tells you that the page is about healthy recipes. Well-organized URLs help search engines understand the content of your pages and make it easier for visitors to navigate your site. Using descriptive words in URLs, rather than random numbers or letters, can also improve your website’s visibility and user experience.
User Experience (UX)
User Experience (UX) is how people feel when they use a website or app. It’s like how enjoyable or easy it is to use a toy or play a game. Good UX means the website or app is simple to navigate, visually appealing, and meets the user’s needs. For example, if a website is easy to find information on and looks nice, people will have a better experience. Improving UX involves making sure everything works well, is easy to understand, and is pleasant to use. A positive UX helps keep visitors on the site longer and makes them more likely to return.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to the actions you take outside of your own website to improve its ranking in search engine results. It’s like promoting a book by telling people about it or getting reviews. Off-page SEO includes activities like getting other websites to link to your site, sharing your content on social media, and improving your site’s reputation. These efforts help search engines see your site as important and trustworthy. The better your off-page SEO, the more likely your site will appear higher in search results, making it easier for people to find you.
Anchor Text Distribution
Anchor text distribution refers to how you spread and use clickable text (anchor text) that links to other pages on your site or external sites. It’s like choosing different labels for boxes in a storage room. Good anchor text distribution involves using various descriptive phrases for links. This helps visitors and search engines understand what each link is about. For example, instead of always using “click here,” use phrases like “learn more about SEO” or “check out our blog.” This improves site navigation, makes your content more informative, and can also boost search engine rankings.
Backlinks
Backlinks are links from other websites that point to your site. They are like votes of confidence from other websites, showing that your content is valuable and worth sharing. For example, if a popular blog links to your article about gardening tips, it’s a backlink. Search engines see backlinks as a sign that your content is trustworthy and relevant. More high-quality backlinks can help improve your website’s ranking in search results, making it easier for people to find your site. However, these backlinks must come from reputable and relevant sites to be most effective.
Blog Commenting
Blog commenting involves leaving a message or comment on someone else’s blog post. It’s like writing a note or sharing your thoughts about a topic in a blog’s comment section. This practice can help you engage with other readers and the blog’s author, and it may also drive traffic to your own website if you include a link in your comment. Blog commenting can improve your website’s visibility and build relationships within your industry. However, it’s important to leave thoughtful and relevant comments rather than spammy ones to make a positive impact and avoid being marked as spam.
Brand Authority

Brand authority is how much people trust and respect a brand because of its reputation and expertise. It’s like being known as the go-to person for a specific topic or skill. For example, if a company is known for providing top-notch advice on fitness, it has strong brand authority in that field. Building brand authority involves consistently delivering high-quality content, being an expert in your industry, and gaining positive reviews and endorsements. A strong brand authority helps attract more customers, improves credibility, and makes it easier for people to choose your brand over others.
Brand Mentions
Brand mentions occur when people or websites talk about or refer to your brand, even without a direct link. It’s like someone mentioning your favorite store in a conversation without giving the store’s website. Brand mentions increase your brand’s visibility and credibility because they show that people recognize and talk about your brand. They also give you chances to engage, thank people, or respond to comments. Tracking brand mentions helps you understand how others perceive your brand. This information can guide you in improving your marketing strategies and connecting better with your audience.
Broken Link Building
Broken link building is a strategy where you find broken links on other websites and offer to replace them with links to your own content. It’s like spotting a missing book in a library and suggesting a new book to fill the spot. To do this, you first find web pages with links that no longer work. Then, you contact the website owners and suggest your own content as a replacement. This helps the website owner fix broken links and also gives you an opportunity to get a valuable backlink to your site. Broken link building improves your site’s visibility and helps both you and the website owner.
Citation Building
Citation building is the process of getting your business’s name, address, and phone number listed on other websites and directories. It’s like making sure your contact information is included in multiple phone books or business listings. These citations help search engines verify your business’s details and improve its visibility in local search results. For example, having your business listed on sites like Yelp or Google My Business can boost your local search rankings. Accurate and consistent citations also help potential customers find your business more easily, which can lead to more visits and calls.
Competitor Link Analysis
Competitor link analysis involves examining the backlinks (links from other sites) that your competitors have to understand their strategies. It’s like studying a sports team’s playbook to learn their tactics. By analyzing where and how competitors get backlinks, you can find opportunities for your own site. For example, if many competitors get links from industry websites, you might target similar sites for your own links. This helps you identify effective strategies in your industry. It also improves your site’s link-building efforts, boosting your search engine rankings.
Content Syndication
Content syndication is sharing your content on other websites or platforms to reach a wider audience. It’s like posting your blog article on different social media sites or news platforms. When you syndicate your content, you allow other sites to republish or link to your original material. This can help attract more readers to your content and increase your website’s visibility. It’s important to make sure that the syndicated content includes a link back to your original site to drive traffic and improve your search engine rankings. Content syndication also helps establish your authority by getting your work seen by more people.
Directory Submissions
Directory submissions involve listing your business or website in online directories or business listings. It’s like adding your name and contact details to a phone book or a directory of local businesses. By submitting your site to directories, you help people find your business more easily and improve your online visibility. This practice also helps search engines understand more about your site and can boost your search rankings. Make sure to choose relevant directories that are related to your industry or location, and ensure that your business information is accurate and consistent across all listings.
Dofollow Links
Dofollow links are clickable links on a webpage that pass on “link juice” or authority to the linked site. They are like endorsements from one site to another, telling search engines that the linked site is valuable. For example, if a blog links to your site with a dofollow link, it helps your site’s ranking in search results because search engines see it as a vote of confidence. These links are important for improving your site’s search engine optimization (SEO) and attracting more visitors. They differ from nofollow links, which do not pass on link juice and don’t affect search rankings.
Domain Authority

Domain Authority is a score that predicts how well a website will rank in search engine results. It’s like a report card that shows how strong a website is compared to others. The score ranges from 1 to 100, with higher numbers meaning a better chance of ranking well. Factors that influence domain authority include the quality and quantity of backlinks, the site’s age, and its overall content quality. A higher domain authority means your site is more likely to appear higher in search results, which can drive more traffic to your site.
Forum Posting
Forum posting involves participating in online forums by writing posts or replies on topics related to your interests or business. It’s like joining a group discussion and sharing your thoughts or answering questions. When you post in forums, you can include links to your website or content, which can help drive traffic and increase visibility. It’s important to contribute valuable and relevant information rather than just promoting your site. Engaging genuinely with forum communities can build your reputation and attract visitors who are interested in what you offer.
Guest Blogging
Guest blogging is when you write a blog post for someone else’s website or blog. It’s like being invited to share your ideas on another person’s platform. In return, you usually get a link back to your own website, which can help drive traffic and improve your search engine ranking. Guest blogging allows you to reach a new audience, build relationships with other bloggers, and showcase your expertise. It’s important to choose blogs that are relevant to your field and provide high-quality content that adds value to their readers.
Influencer Outreach

Influencer outreach involves connecting with popular individuals or personalities in your industry to promote your brand or content. It’s like asking a well-known person to recommend your product or service. You reach out to influencers who have a large and engaged following on social media or blogs, and ask them to share your content or collaborate on a project. This can help you reach a bigger audience, build credibility, and drive more traffic to your website. Effective influencer outreach involves choosing the right influencers, creating a compelling message, and offering something valuable in return for their support.
Link Building
Link building is the process of getting other websites to link to your own. It’s like making connections and asking others to recommend your site. When other sites link to your pages, it helps increase your website’s credibility and can improve its ranking in search engine results. There are various ways to build links, such as creating high-quality content that others want to share, reaching out to other websites for guest posts, or getting listed in online directories. The more reputable and relevant the sites linking to you, the better it is for your site’s visibility and search engine optimization.
Link Exchange
Link exchange is when two websites agree to link to each other’s content. It’s like trading bookmarks with a friend so you both have access to each other’s favorite sites. For example, if you run a cooking blog and another site about food agrees to link to your recipes, you would link back to their site in return. This can help both sites get more traffic and improve search engine rankings. However, it’s important to exchange links with relevant and high-quality sites to avoid any negative impact on your website’s reputation and search ranking.
Link Juice
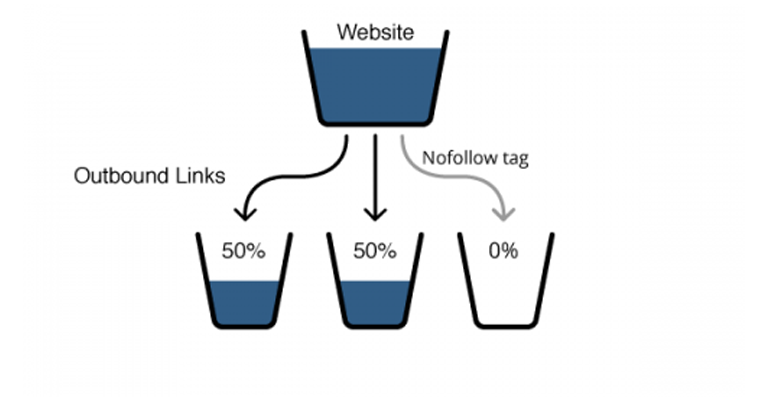
Link juice is the value or authority a link passes from one website to another. It’s like transferring a vote of confidence from one site to another. When a reputable site links to your page, it sends some of its authority or “juice” to your site, which can help improve your search engine ranking. The more link juice you get from high-quality and relevant sites, the better your site can rank in search results. Link juice helps search engines determine the importance and trustworthiness of your site based on the links it receives.
Link Profile
A link profile is a collection of all the links pointing to your website. It’s like a list of all the roads that lead to your house. This profile includes the types of links, where they come from, and how trustworthy those sources are. A strong link profile has links from many different and reputable websites, showing that your site is popular and valued. Monitoring your link profile helps you understand how well your site is connected to other sites and can help you improve your search engine ranking. A good link profile supports better visibility and credibility in search results.
Local Listings
Local listings are online directories where businesses can provide their contact information, address, and other details. It’s like putting your business’s name, phone number, and address in a local phone book or directory. Examples of local listings include Google My Business, Yelp, and Bing Places. These listings help people find your business when they search for services or products in their area. Having accurate and complete local listings makes it easier for potential customers to find you and can improve your visibility in local search results. It’s important to keep your information updated and consistent across all listings.
Nofollow Links
Nofollow links are clickable links that do not pass on any authority or “link juice” to the linked website. It’s like a recommendation that says, “This link is here, but don’t give any extra points for it.” When a website uses a nofollow link, it tells search engines not to count it as a vote of confidence for the linked site. Nofollow links are often used for advertisements, comments, or other places where the site owner doesn’t want to endorse the linked content. While they don’t directly boost search rankings, they can still drive traffic to your site and provide exposure.
Off-Page SEO Audit
An off-page SEO audit focuses on evaluating factors outside your website that influence search engine rankings. It examines backlinks, which are links from other websites pointing to yours, to assess their quality and relevance. The audit also reviews your social media presence, brand mentions, and online reputation. Additionally, it looks at the trustworthiness of the websites linking to yours, ensuring they aren’t spammy or harmful. The goal is to strengthen external signals that boost your site’s authority and improve search visibility.
Online Reputation Management

Online reputation management is the process of controlling and improving how people see your business or personal brand on the internet. It’s like making sure that people hear good things about you or your company when they look online. This involves monitoring what is being said about you, responding to reviews, and promoting positive content. For example, if someone posts a negative review, you might respond politely to resolve the issue. By managing your online reputation, you help build trust with customers and ensure that the positive aspects of your brand are visible and highlighted.
Page Authority
Page Authority is a score that predicts how well a specific webpage will rank in search engine results. It’s like a report card for just one page on your website. The score ranges from 1 to 100, with higher numbers meaning a better chance of showing up at the top of search results. Factors that affect page authority include the quality of links to that page, the content on the page, and how relevant it is to search queries. A higher page authority means that search engines are more likely to consider your page as important and useful for users looking for related information.
PBN (Private Blog Network)
A PBN, or Private Blog Network, is a group of websites that are controlled by one person or organization to create backlinks to a main website. It’s like having several friends who each give a recommendation for your business. The goal is to boost the main site’s search engine ranking by linking to it from these other sites. However, using a PBN can be risky because search engines may view it as a way to manipulate rankings. If caught, it can lead to penalties or lower search rankings. It’s important to use ethical methods for building backlinks and improving your website’s visibility.
Press Release

A press release is a written announcement that shares important news or updates about a company or organization with the media and the public. It’s like sending a letter to newspapers and news websites to let them know about something newsworthy. Press releases usually include details about an event, product launch, or other significant news, and are designed to get attention from journalists and news outlets. The goal is to spread information widely and generate media coverage, which can help increase visibility and improve the public’s perception of the company or event being announced.
Referral Traffic
Referral traffic consists of the visitors who come to your website by clicking on a link from another site. It’s like when someone tells their friend about your favorite store, and the friend visits that store because of the recommendation. For example, if a blog writes about your business and includes a link to your website, the people who click on that link and visit your site are counted as referral traffic. This type of traffic is valuable because it shows that other sites are recommending your content or services, which can help increase your site’s visibility and attract more visitors.
Resource Page Link Building
Resource page link building is the process of getting your website linked from pages that list helpful resources or tools. It’s like being added to a list of recommended websites or guides on a particular topic. For example, if a website has a page with links to useful sites about gardening, and your site offers gardening tips, you would want to be included on that list. This can help drive more visitors to your site and improve your search engine ranking. To succeed with resource page link building, find relevant pages that fit your content, and reach out to request a link.
Skyscraper Technique

The Skyscraper Technique is a method for improving your website’s search engine ranking by creating better content than what currently ranks highest on search engines. It’s like building a taller, better-looking skyscraper to stand out in a city of buildings. First, find popular content in your industry that performs well. Next, create something even better—more detailed, more useful, or more engaging. Finally, reach out to the sites that linked to the original content and ask them to link to your improved version instead. This technique helps attract more visitors and boosts your site’s visibility by offering superior content.
Social Bookmarking
Social bookmarking is the practice of saving and sharing links to your favorite websites or pages on social bookmarking sites. It’s like keeping a list of important websites and sharing it with others. For example, you might use a site like Pinterest or Reddit to save and organize links to articles, blog posts, or videos. When you bookmark a link, it can be seen by others who visit the same site, which can help drive traffic to your website and increase its visibility. This also helps with SEO by showing search engines that your content is valued and shared.
Social Signals
Social signals are the likes, shares, comments, and overall engagement your content receives on social media platforms. It’s like getting a thumbs-up or a lot of attention from people on social media. When your posts are liked, shared, or commented on, it shows that people are interested in your content. Search engines may use these signals to understand how popular or valuable your content is. More social signals can lead to better search rankings because they suggest that your content is relevant and engaging to a lot of people.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO refers to the optimization of a website’s backend and structure to improve its visibility in search engines. It includes tasks like improving site speed, ensuring mobile-friendliness, and making sure search engines can easily crawl and index your site. Technical SEO also involves setting up proper URL structures, using HTTPS for security, and fixing any broken links or errors. These efforts help search engines understand and rank your site better. Strong technical SEO is essential for a smooth user experience and better search engine rankings.
301 Redirects

A 301 redirect is a way to send visitors and search engines from one webpage to another permanently. It’s like moving from one house to another and making sure your mail gets forwarded to your new address. When you set up a 301 redirect, it tells the web browser and search engines that the old page has moved to a new location, so they should go to the new URL instead. This helps preserve the search engine rankings and traffic from the old page, making sure you don’t lose visitors or SEO value when you change your website’s structure or content.
404 Error Pages
A 404 error page appears when someone tries to visit a webpage that doesn’t exist anymore. It’s like showing up at a house that has been torn down. When a user clicks on a link to a page that has been moved or deleted, they see a 404 error page, which tells them that the page can’t be found. This can be frustrating for visitors, so it’s a good idea to have a helpful 404 page that guides them to other parts of your website or offers a search function. Properly managing 404 errors helps keep visitors on your site and improves their overall experience.
AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages)
AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) is a technology designed to make web pages load faster on mobile devices. It’s like a shortcut that helps web pages appear quickly on smartphones and tablets. AMP pages are stripped-down versions of regular web pages, with less complex code and smaller file sizes, so they can be displayed almost instantly. This is helpful for users who are on the go and want to view content without long wait times. By using AMP, you can improve user experience and increase the chances that people will stay on your site rather than leave due to slow loading times.
Canonicalization
Canonicalization is the process of choosing the best version of a web page when there are multiple pages with similar content. It’s like picking the main address for a house when there are several similar addresses. For example, if your website has two pages with nearly the same content, canonicalization tells search engines which one is the “official” version to show in search results. This helps prevent problems with duplicate content and ensures that your site’s SEO benefits are not spread too thin. By using canonical tags, you make sure that search engines know which page to focus on, improving your site’s visibility and ranking.
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a system of servers that work together to deliver website content quickly to users all around the world. It’s like having multiple delivery trucks that can bring a package to you faster, no matter where you live. When you use a CDN, copies of your website’s files are stored on different servers in various locations. When someone visits your site, the CDN delivers the files from the server closest to them. This speeds up the loading time of your website and improves the user experience, especially for people who are far from your main server.
Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are important measures that help assess a website’s user experience by focusing on three key areas: loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability. They include Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which measures how quickly the main content of a page loads; First Input Delay (FID), which tracks how soon users can interact with the page; and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), which looks at how much the page layout shifts during loading. These metrics are crucial for ensuring that your website is fast, responsive, and user-friendly, leading to a better overall experience for visitors.
Crawlability
Crawlability is how easily search engines can visit and explore your website’s pages. It’s like letting search engine robots walk through your house to see all the rooms. If a website is crawlable, it means search engines can follow links on the site and index the content so it can appear in search results. Good crawlability ensures that all important pages on your site are discovered and understood by search engines, which can help improve your site’s visibility and ranking in search results.
hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags are special HTML codes used to tell search engines which language and regional version of a page to show users based on their location and language preferences. It’s like giving directions to different versions of a book for readers in various countries. For example, if you have a webpage in English for the US and another in French for Canada, hreflang tags help search engines show the right version to the right audience. This improves user experience by ensuring that people see content in their preferred language and relevant to their region.
HTTP Headers
HTTP headers are pieces of information sent between a web server and your browser when you access a website. They are like notes that provide details about the webpage or how it should be handled. For example, HTTP headers can tell your browser how to display the page, how long to keep it in its memory, or whether to redirect you to another page. They help with tasks like setting security rules, managing cookies, and improving website performance. By using the right HTTP headers, you can enhance the security and efficiency of your website.
HTTPS (SSL Certificate)

HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) with an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a way to keep data safe when you visit a website. It’s like a secure lock on a diary that only you can open. When a website uses HTTPS, it encrypts the information exchanged between your browser and the website, making it hard for others to see or steal. This is especially important for protecting sensitive information like passwords or credit card numbers. An SSL certificate helps verify that the website is genuine and not a scam, providing a safer browsing experience.
Indexability
Indexability is how easily search engines can find and add your web pages to their search index. It’s like making sure a librarian can find and list all the books in a library. For a website to be indexable, its pages need to be accessible to search engine bots and not blocked by rules or errors. Good indexability ensures that search engines can see and understand your content, which helps your site appear in search results. To improve indexability, make sure your website’s pages are well-structured and free from technical issues that might prevent search engines from accessing them.
International SEO
International SEO is the practice of optimizing your website to rank well in search engines across different countries and languages. It’s like making sure your website can be understood and found by people all over the world. This involves adjusting your website’s content, keywords, and structure to target specific regions or languages. For example, you might create separate pages for different countries or use hreflang tags to show the right version of your site to users based on their location. By using international SEO, you help search engines deliver the most relevant content to users in various regions, improving your global reach and visibility.
JavaScript Rendering
JavaScript rendering is the process of generating and displaying content on a webpage using JavaScript. It’s like building a model with instructions that are followed step-by-step to create the final product. When a webpage uses JavaScript rendering, the content is created or updated by JavaScript code after the initial page load. This can help create dynamic and interactive websites, but it can also make it harder for search engines to see and index the content. To ensure search engines can find and rank your content, it’s important to make sure that the JavaScript-rendered content is accessible and properly indexed.
Lazy Loading

Lazy loading is a technique used to improve a website’s performance by only loading images or other content when they are needed, rather than all at once. It’s like waiting to unpack your suitcase until you actually need the items. For example, on a long web page with many images, lazy loading will only load the images that are visible on the screen and will load others as you scroll down. This helps the page load faster and saves bandwidth, making the user experience smoother and more efficient.
Log File Analysis
Log file analysis is the process of examining server logs to understand how people are interacting with your website. Think of it like reviewing a diary to see what happened each day. Server logs are files that record every visit to your site, including details like which pages were viewed, how long users stayed, and if there were any errors. By analyzing these logs, you can find patterns, identify issues, and improve your website’s performance and user experience. This helps you understand what’s working well and what needs fixing.
Minification (CSS, JavaScript)
Minification is the process of reducing the size of your website’s code files by removing unnecessary characters, like spaces and comments. It’s like trimming down a long document to make it shorter and easier to handle. For example, minification can be applied to HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files. This makes the files smaller and faster to load, which helps your website run more smoothly and quickly. By using minification, you improve your site’s performance and reduce the amount of data users need to download.
Mobile-Friendliness
Mobile-friendliness means that a website is designed to work well on smartphones and tablets. It’s like making sure a book can be easily read on any device, whether it’s a big screen or a small one. A mobile-friendly website adjusts its layout, text size, and images so that it looks good and is easy to use on smaller screens. This includes having buttons that are easy to tap and content that doesn’t require zooming. Ensuring mobile-friendliness helps improve the user experience for people browsing on their phones and can also boost your site’s ranking in search engines.
Page Speed Insights
Page Speed Insights is a tool that measures how quickly a webpage loads and provides suggestions for making it faster. It’s like a report card that tells you how well your website performs and what you can do to improve. When you use Page Speed Insights, it checks various factors, such as how fast the page’s content appears and how long it takes for the page to become interactive. The tool then gives you tips to help speed up your website, like optimizing images or reducing code. Faster page speed improves user experience and can help your site rank better in search results.
Pagination
Pagination is the way of dividing a large amount of content into separate pages or sections on a website. It’s like breaking a big book into chapters. For example, if you have many blog posts or product listings, pagination helps by showing a few items per page and letting users navigate through the rest by clicking on “Next” or page numbers. This makes it easier for visitors to find and view content without having to scroll through a long, endless list. Pagination also helps search engines understand and index your content more effectively.
Render-Blocking Resources
Render-blocking resources are files, like JavaScript or CSS, that must be fully loaded before a webpage can display its content. It’s like waiting for the setup crew to finish their work before you can start watching a movie. When these resources are render-blocking, they slow down how quickly the page appears to users. To improve page speed, it’s important to manage or minimize these resources, so the page can load and display content faster. This can involve techniques like deferring non-essential scripts or optimizing CSS to ensure a quicker and smoother user experience.
Robots.txt
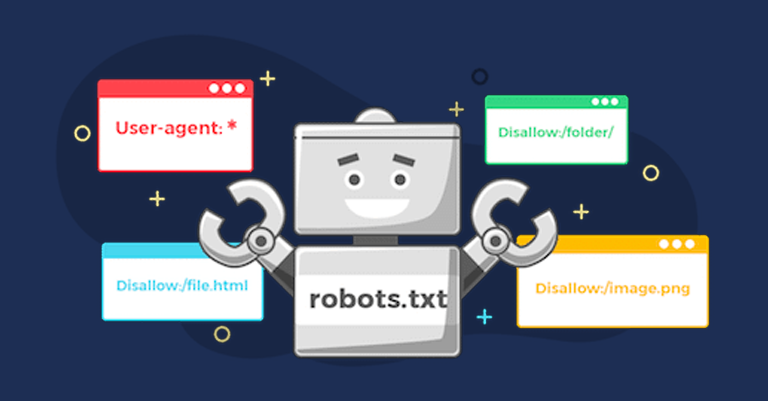
Robots.txt is a file that tells search engines which parts of your website they can or cannot visit. It’s like giving instructions on which rooms in a house are open for a tour and which ones are off-limits. When search engines visit your site, they check the robots.txt file to see which pages they should ignore or focus on. By using this file, you can control what search engines see and ensure they only index the content you want them to, helping manage your site’s visibility in search results.
Schema Markup
Schema markup is a special code you add to your website to help search engines understand your content better. It’s like adding labels to a box of toys to explain what’s inside. For example, if you have a recipe on your site, schema markup can provide details like cooking time, ingredients, and ratings. This extra information helps search engines display richer, more useful results, such as star ratings or recipe details, which can make your site stand out in search results and attract more visitors.
Server Response Time
Server response time is how long it takes for a web server to send a response after receiving a request from your browser. It’s like how long you wait for a waiter to bring your food after you order. If the server response time is quick, your webpage loads faster, and visitors have a better experience. If it’s slow, your site can be sluggish and frustrating to use. Improving server response time helps your website run more smoothly and efficiently, making it more enjoyable for users.
Site Architecture
Site architecture is the way a website is organized and structured. It’s like the blueprint of a house, showing how rooms and hallways are laid out. Good site architecture makes it easy for visitors to find what they’re looking for and helps search engines understand the content and structure of your site. It involves arranging pages in a clear hierarchy, using categories and subcategories, and creating a logical navigation system. Proper site architecture improves user experience and helps with better search engine rankings by making your content more accessible and easier to index.
Site Speed
Site speed is how fast a website loads and displays its content when you visit it. It’s like how quickly a book opens to the page you want to read. A fast site speed means your pages appear quickly, which makes for a better experience for visitors. If a site is slow, users may become frustrated and leave before the page even loads. Improving site speed involves optimizing images, reducing the size of files, and using fast servers to ensure that pages load quickly and smoothly.
Structured Data
Structured data is a way of organizing and labeling information on your website so search engines can understand it better. It’s like putting labels on your boxes to explain what’s inside. For example, if you have a recipe on your site, structured data can tell search engines details like the ingredients, cooking time, and nutrition facts. This helps search engines show richer, more detailed results in search results, like showing star ratings or cooking times. Using structured data can make your site stand out and attract more visitors by providing extra information in search results.
URL Parameters
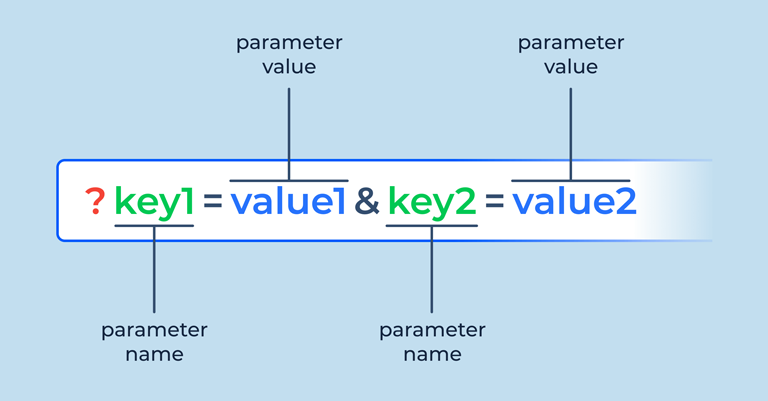
URL parameters are extra pieces of information added to a web address to pass data between pages or track user activity. They look like extra parts of the URL that come after a question mark, such as `?category=books&sort=price`. URL parameters are used to filter or sort content, like showing specific products or sorting search results. They help websites provide personalized experiences or track how users interact with the site. However, too many parameters or incorrect use can make URLs complex and harder for search engines to understand, so it’s important to use them wisely.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website to help search engines find and index them. It’s like a map that shows where every page is located, making it easier for search engines to understand and crawl your site. The XML sitemap provides information about each page, such as when it was last updated and how important it is compared to other pages. This helps search engines discover new or updated content quickly, improving the chances of your site being included in search results.
Content SEO
Content SEO focuses on creating and optimizing content to improve its visibility in search engine results. This involves using keywords strategically, ensuring the content is valuable and relevant to the target audience, and organizing it with clear headings and structure. Content SEO also includes updating and refreshing older content to keep it current. The goal is to produce high-quality content that attracts and engages users while ranking well in search engines. Effective content SEO helps drive organic traffic and supports overall SEO efforts.
Competitor Content Analysis
Competitor content analysis is the process of reviewing and examining the content your competitors publish on their websites. It’s like checking out what other students are writing in their essays to see what’s popular and effective. This analysis helps you understand what topics they cover, how they structure their content, and what strategies they use to engage their audience. By studying your competitors, you can find gaps in their content, discover new ideas, and improve your own content to stand out and attract more visitors to your site.
Content Audit

A content audit is a review of all the content on your website to evaluate its quality, relevance, and performance. It’s like going through your closet to decide what clothes you want to keep, update, or throw away. During a content audit, you check things like how well your pages are performing, if they’re up-to-date, and if they still meet your goals. This helps you identify which content needs improvement, which can be removed, and what new content might be needed to enhance your website’s effectiveness and user experience.
Content Brief
A content brief is a document that outlines the key details and goals for creating a piece of content. It’s like a set of instructions for writing an article or blog post. The brief usually includes information such as the topic, target audience, main points to cover, keywords to use, and the overall purpose of the content. By following the content brief, writers can produce content that meets specific requirements and helps achieve the desired outcomes, like engaging readers or improving search engine rankings.
Content Calendar
A content calendar is a schedule that helps you plan and organize the content you will publish over time. It’s like a planner for your blog posts, social media updates, and other types of content. The calendar shows when each piece of content will be published and what it will be about. It helps you keep track of deadlines, stay consistent with posting, and ensure that your content aligns with important dates or events. Using a content calendar makes it easier to manage your content strategy and keep your audience engaged.
Content Curation

Content curation is the process of finding, selecting, and sharing content from other sources that you think will be interesting or useful to your audience. It’s like being a DJ who picks and plays the best songs for your listeners. Instead of creating all new content, you gather, and present valuable information, articles, or media created by others. This helps keep your audience informed and engaged while showing that you stay current with relevant topics. Engaging in content curation also saves time and builds your credibility by sharing high-quality and relevant information with your followers.
Content Distribution
Content distribution is the process of sharing and promoting your content to reach a wider audience. It’s like putting up flyers in different places to let more people know about your event. This can include posting your content on social media, sending it through email newsletters, or sharing it on other websites. Effective content distribution helps ensure that your content is seen by as many people as possible, increasing its reach and impact. By choosing the right channels and strategies, you can attract more visitors and engage with your audience more effectively.
Content Engagement
Content engagement refers to how people interact with your content. It’s like watching how people react to a movie or show you’ve made. Engagement includes actions like liking, sharing, commenting, or spending time reading your content. High content engagement means that your audience is interested and involved, which can lead to more visibility and better results for your content. By creating engaging content and encouraging interactions, you can build stronger connections with your audience and keep them coming back for more.
Content Gap Analysis
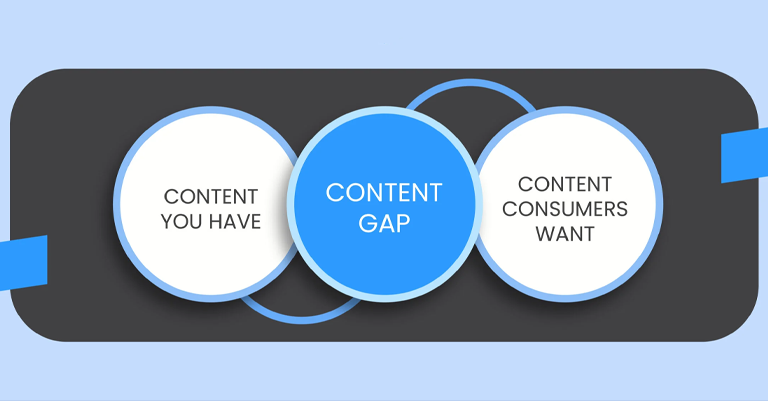
Content gap analysis is the process of finding missing or underdeveloped topics on your website compared to what your audience or competitors are offering. It’s like checking if there are empty spaces in your puzzle. You look at the content you have and compare it with what’s needed or what others are providing. This helps you discover areas where you can create new content or improve existing content to better meet your audience’s needs and stand out from competitors. Filling these gaps can help attract more visitors and keep your content relevant and useful.
Content Gap Filling
Content gap filling is the process of creating new content to address topics or questions that are missing from your website. It’s like adding pieces to a puzzle to make it complete. After identifying gaps in your content through analysis, you create articles, blog posts, or other resources to cover those missing areas. This helps ensure that your website provides comprehensive and valuable information for your audience. By filling these gaps, you can attract more visitors, improve user satisfaction, and stay ahead of your competitors.
Content Ideation
Content ideation is the process of coming up with new ideas for content that you want to create and share. It’s like brainstorming for a school project or a fun activity. During content ideation, you think about topics that will interest your audience, solve their problems, or entertain them. This helps you generate fresh and relevant content ideas that can engage your audience and keep your content strategy on track. Good content ideation involves researching trends, understanding audience needs, and exploring different formats to find the best ideas for your content.
Content Marketing Strategy
A content marketing strategy is a plan for creating and sharing content to attract and engage your target audience. It’s like a roadmap that guides you on what type of content to create, where to share it, and how to measure its success. The strategy includes setting goals, understanding your audience, choosing the right content types, and deciding how to distribute and promote your content. By following a content marketing strategy, you can effectively reach your audience, build relationships, and achieve your business objectives.
Content Optimization

Content optimization is the process of improving your content so that it performs better and is easier for people to find and enjoy. It’s like fine-tuning a recipe to make it taste just right. This includes making sure your content is clear, relevant, and useful, as well as using keywords that help it appear in search results. You might also adjust the format, add images, or make sure it loads quickly on different devices. By optimizing your content, you make it more engaging for your audience and increase its chances of being seen and shared.
Content Outline
A content outline is a plan that shows the structure and main points of your content before you start writing. It’s like a blueprint for a house that guides you on where to put each room. The outline includes headings and subheadings that break down your topic into sections, and it helps you organize your ideas and information in a logical order. By creating a content outline, you ensure that your writing stays focused, covers all the important points, and is easy to follow for your readers.
Content Personalization
Content personalization means creating special content just for each person who sees it. Imagine you’re giving a gift, and you choose something that matches what each friend likes. Similarly, content personalization uses what we know about each person, like their interests or past activities, to make the content more interesting and relevant. For example, if someone likes pets, they might see articles about pet care. This makes the content more engaging and enjoyable for each individual, helping them feel more connected to what they’re reading or watching.
Content Quality
Content quality is about making sure your content is excellent and helpful for the people who read it. It means your content should be correct, clear, and interesting. Think of it like this: if you’re making a drawing, you want it to be neat and colorful so that everyone enjoys looking at it. High-quality content should provide valuable information, be free of mistakes, and be easy to understand. Good content keeps readers interested and helps them find what they need quickly.
Content Refresh

Content refresh means updating old content to make it new and useful again. Just like fixing up an old toy to make it work better, refreshing content involves adding new information, correcting errors, or changing the way it’s presented. This can include updating facts, adding new images, or improving the text to make it clearer. The goal is to keep the content relevant and engaging so that it continues to be useful for readers and performs well in search engines.
Content Repurposing
Content repurposing is when you take old content and use it in new ways. Imagine you have a story you wrote for a school project, and you turn it into a video or a series of pictures. This is what repurposing does— it takes existing ideas and presents them in different formats, like turning a blog post into a social media post or a podcast. It helps you reach more people and make the most of the content you’ve already created, saving time and effort while keeping things fresh.
Content Updates
Content updates involve making changes to old content to keep it accurate and relevant. It’s like fixing an old book by adding new chapters or correcting mistakes. When you update content, you check for outdated information, add new facts, and make improvements to ensure it still meets the needs of your audience. This process helps keep the content fresh and useful, making sure that readers get the best and most current information when they come back to it.
Content-Length
Content-Length is a term that tells us how big a piece of content is. It’s like measuring the length of a pencil to know how long it is. When we talk about content length, we mean counting how many words or how much space a piece of content takes up. This helps us understand how much information is in the content and how long it might take to read or view it. For example, a short story might have a small content length, while a big report could have a large content length. Knowing this helps in organizing and displaying content correctly on a website or other platforms.
Evergreen Content

Evergreen content is the kind of information that stays useful and important for a long time. Imagine a tree that stays green all year round; that’s what evergreen content does. It doesn’t get old or out of date quickly. For example, a blog post about how to tie your shoes will always be helpful because the steps don’t change. People can read it anytime, and it will still make sense. This kind of content keeps bringing visitors to a website because it answers questions that people will always have. It’s like having a book that people keep wanting to read over and over again.
Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are special boxes that appear at the top of search results on Google. They give a quick answer to a question someone asks. For example, if you search for “What is the tallest mountain?” the featured snippet might show a short paragraph that says, “Mount Everest is the tallest mountain at 29,032 feet.” These snippets often include a small piece of text, a list, or even a picture to help explain the answer. Google picks these answers from websites that do an excellent job of explaining things clearly. It’s like getting the best answer right away without having to click on a link.
Keyword Mapping
Keyword mapping is a way to match specific words or phrases, called keywords, to the right pages on a website. Think of it like making a treasure map where each keyword points to the page where the treasure (information) is found. For example, if you have a page about “how to bake cookies,” you would want to use keywords like “cookie recipe” or “baking tips” on that page. This helps search engines like Google understand what each page is about and show it to the right people when they search. It’s a way to organize a website so visitors can easily find what they’re looking for.
Keyword Research
Keyword research is the process of finding the words or phrases people use when they search for something online. Imagine you’re trying to figure out what people are most interested in, like what toys they want to buy. You would listen to what they ask for most often. In the same way, keyword research helps you understand what topics are popular. By knowing the right keywords, you can create content that matches what people are searching for. This makes it easier for them to find your website. It’s like choosing the best words to help others discover what they need.
Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases people use when searching online. Imagine you want to buy a blue toy car instead of just any toy car. Instead of searching for “toy car,” you might type “small blue toy car with remote control.” That’s a long-tail keyword. These keywords may not be searched as often as shorter ones, but they help you find exactly what you want. For website owners, using long-tail keywords means attracting visitors who know what they’re looking for, making it easier to meet their needs. It’s like being very clear about what you want, so you find the right thing faster.
Multimedia Content
Multimedia content is any online content that uses different forms of media, like pictures, videos, music, or animations, to share information. Imagine reading a storybook with words, colorful pictures, sound effects, and even a short movie that plays on the page. That’s what multimedia content is like on the internet. Instead of just reading text, you can watch videos, listen to music, or see charts and graphs that help explain things better. Websites use multimedia content to make information more interesting and easier to understand, especially for people who like to see or hear things instead of just reading.
Pillar Content
Pillar content is a main, detailed article or page on a website that covers a big topic in depth. Imagine it like the strong pillars that hold up a building. This content acts as the foundation for other smaller articles that connect to it. For example, if a website is about gardening, the pillar content might be an article called “The Ultimate Guide to Growing a Garden.” This article would cover many aspects of gardening, like planting, watering, and choosing the right plants. Then, smaller articles can dive deeper into each of these topics. Pillar content helps visitors find lots of useful information in one place and keeps them exploring the website.
Search Volume
Search volume is the number of times people type a specific word or phrase into a search engine like Google over a certain period, usually a month. Imagine you’re trying to see how many kids ask for a certain toy. If a lot of kids ask for the toy, it has a high search volume. If only a few ask, it has a low search volume. Knowing the search volume helps people who create websites understand how popular a keyword is. This way, they can choose the right words to use in their content, so more people can find their website when they search online.
SERP Features
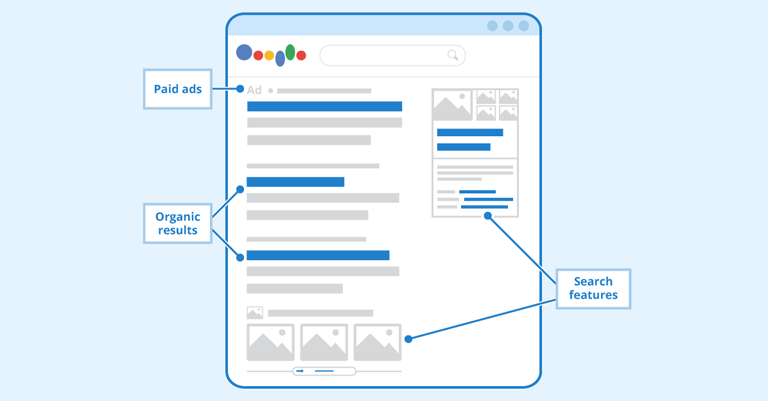
SERP features are special parts of a search engine results page (SERP) that give extra information beyond the usual list of links. When you search for something on Google, you might see things like a box with a quick answer, maps, images, or even a list of questions and answers. These are all SERP features. For example, if you search for the weather, you’ll see a weather box at the top with today’s forecast. SERP features help you find what you need faster, without clicking through different websites. They make searching easier by showing you useful information right away.
User Intent
User intent is what someone really wants to find or do when they search for something online. Imagine you ask for ice cream. Are you looking to buy it, make it, or learn about different flavors? That’s your intent. When people type words into a search engine, they have a goal in mind. They might want to buy something, find information, or visit a website. Understanding user intent helps website owners create content that matches what people are truly looking for. If a website matches user intent well, it will show up higher in search results, helping people find exactly what they need.
